Multifocal Choroiditis Fa

Journal Of Ophthalmic Science Open Access Pub

Multimodal Imaging Of A 29 Year Old Woman With Multifocal Choroiditis Download Scientific Diagram

Imageology Features Of Different Types Of Multifocal Choroiditis Semantic Scholar

Indocyanine Green Angiography In Posterior Uveitis Abstract Europe Pmc

Multifocal Choroiditis Recognizing Pathology Optos

Indocyanine Green Angiography In Posterior Uveitis Agrawal Rv Biswas J Gunasekaran D Indian J Ophthalmol
Multifocal choroiditis (MFC) presents most frequently in female patients with an age range of 6 to 69 years, with the average age of presentation in the fourth decade of life Most patients are moderately myopic, and the majority of patients are affected bilaterally Punctate inner choroidopathy (PIC) also has a predilection for myopic female patients, but it tends to affect somewhat younger patients, with a mean age of onset of 26 years (range 1640 years).
Multifocal choroiditis fa. Multifocal Choroiditis and Panuveitis MCP is a condition characterized by intraocular inflammation and multifocal choroidal lesions occurring in the absence of any known ocular or systemic disease The disease is typically bilateral and seems to have a predilection for females in the second to sixth decades of life, with a median age of 28 to 33 years. Rationale Optical coherence tomography angiography (OCTA) has the advantage to visualize the microvascular structure of the retina in vivo and was utilized clinically in various neovascular retinal diseases The OCTA has also been used to examine the lesion in multifocal choroiditis and panuveitis (MCP) This study aimed to describe a case of MCP and present the disease process of a punched. Multifocal choroiditis (MFC) is an inflammatory disorder characterized by swelling of the eye (called uveitis) and multiple lesions in the choroid, a layer of blood vessels between the white of the eye and the retina Symptoms include blurry vision, floaters, sensitivity to light, blind spots and mild eye discomfort.
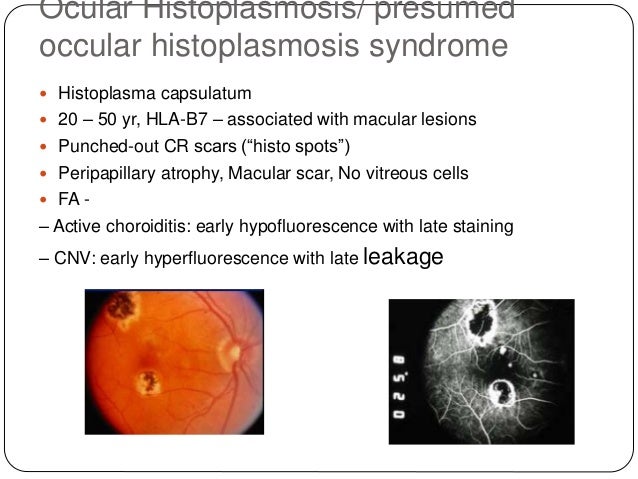
Multifocal choroiditis and panuveitis syndrome, and the idiopathic subretinal fibrosis syndrome are considered entities along one spectrum and treatment does not differ much between them With a diagnosis of multifocal choroiditis and panuveitis, oral cyclosporine A 3 mg/kg per day and prednisolone 25 mg per day, along with topical betamethasone QID and tropicamide TDS were initiated in both eyes. Idiopathic multifocal choroiditis is a chronic and progressive bilateral inflammatory disease that may be associated with choroidal neovascularization and chorioretinal atrophy The commonly affected sites are the retinal pigment epithelium (RPE), outer retinal spaces, choriocapillaris, and, less commonly, the choroidal stroma. • A review of 28 cases of multifocal choroiditis with vitreous inflammatory cells demonstrates that these patients have chorioretinal scars similar to those in the presumed ocular histoplasmosis syndrome (POHS), but they have a low incidence of positive histoplasmin skin test reactions and calcified granulomata on chest xray films.
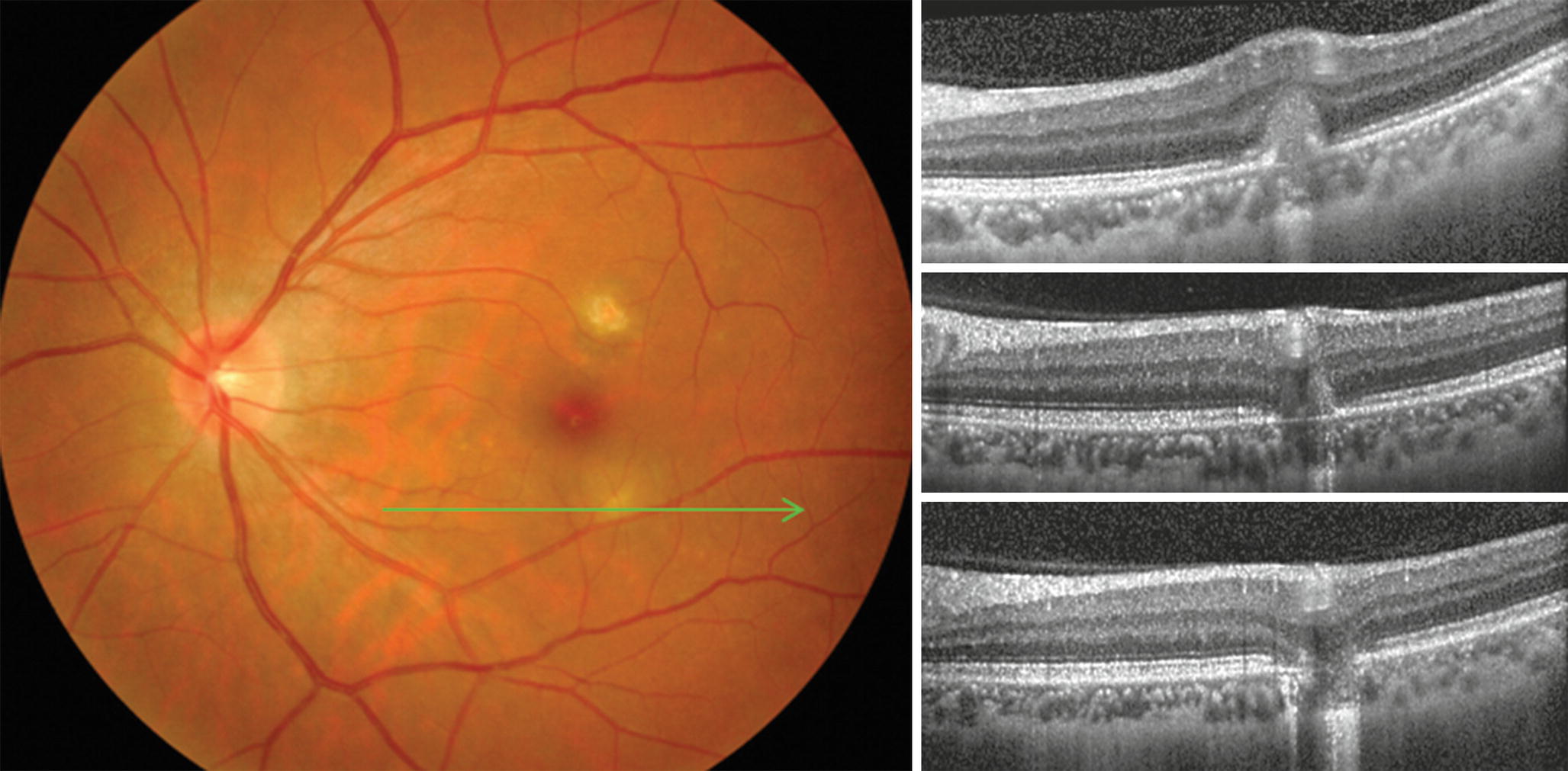
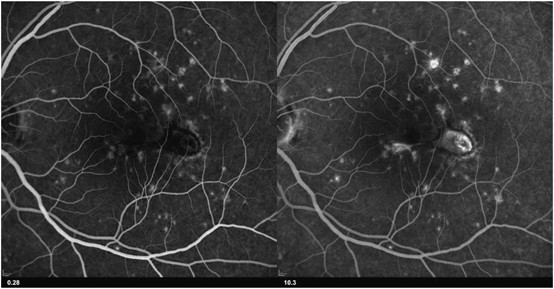
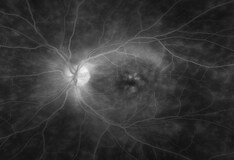
Multifocal choroiditis (MFC) is characterized by small multiple yellowish choroidal lesions of the posterior pole, and it may be associated with panuveitis MFC is often bilateral, and. Early (A) and late (B) phase of fluorescein angiography (FA) of a patient with multifocal choroiditis shows a welldemarcated area of hyperfluorescence (arrows) and late leakage, indicative of. Multifocal choroiditis (MFC) is an inflammatory condition, occasionally associated with choroidal neovascularization (CNV) Bevacizumab (Avastin) and ranibizumab (Lucentis) are therapies that.
Characteristic fundus lesions are described as multifocal, creamcolored, and ovoid and appear at the level of the RPE and choroid They typically measure microns, and often extend radially from the optic nerve to cover the postequatorial nasal retina. Multifocal choroiditis and panuveitis syndrome Although HL may be negative in 4 to 10% of cases with birdshot chorioretinopathy, certain findings are in favor of multifocal choroiditis and panuveitis syndrome The hypofluorescent spots on ICG angiography in this case are smaller, of unequal sizes and more randomly distributed than what is seen. Multifocal choroiditis Use of the terms idiopathic multifocal choroiditis, multifocal choroiditis with panuveitis (MFCPU), recurrent multifocal choroiditis (RMC), punctate inner choroiditis or choroidopathy (PIC), and pseudopresumed ocular histoplasmosis syndrome (pseudoPOHS), among others, is both inconsistent and confusing in the literature.
Abstract Punctate inner choroidopathy (PIC) is a relatively uncommon inflammatory multifocal chorioretinopathy that predominantly affects young, myopic women Subfoveal choroidal neovascularization (CNV) often leads to rapid loss of sight Fluorescein angiography (FA) and indocyanine green angiography (ICGA) remain the existing gold standards for CNV diagnosis. Notably, all the lesions detected by FA, AF and OCT corresponded to focal areas of hypofluorescence seen on ICGA, whereas several additional hypofluorescent areas that were not associated with FA, AF or OCT abnormalities, were also detected with ICGA Multifocal Choroiditis Multimodal Imaging Retinal Diseases / diagnosis*. Multifocal choroiditis with panuveitis (MCP) is a chronic, bilateral disease that generally affects young, healthy individuals, especially myopic females between the third and fifth decade of life Patients com47, plain of blurred vision, floaters and/or scotoma They may also experience photopsias.
Punctate inner choroidopathy (PIC) is an inflammatory disorder that primarily affects the choroid (vascular layer) of the eye It most commonly occurs in young, nearsighted (myopic) women The symptoms and severity may vary from person to person. Granulomatous lesions have been described in 80% of patients and can be associated with peripheral choroiditis (6, 7) Peripheral multifocal choroiditis (PMC) occurs mainly in women >55 years of age and is characterized by peripheral punched‐out lesions associated with intraocular inflammation (Figure 1) Posterior uveitis may be sight‐threatening when associated with inflammation of the posterior pole and with cystoid macular edema (CME). Multifocal choroiditis is a rare idiopathic inflammatory disease that affects the choroid Click on sample images to enlarge or download Multifocal Choroiditis, California, FA OS, Courtesy Paulo Stanga, MD.
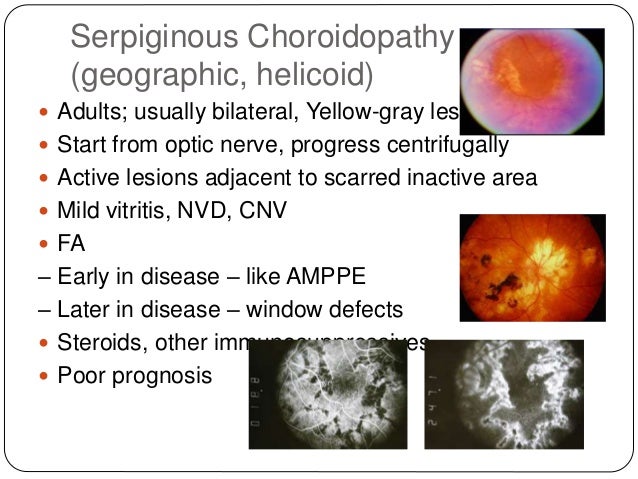
Multifocal, creamy choroidal infiltrates in older patients can be due to a masquerade syndrome (see Chapter 30) 44 Patients with familial juvenile systemic granulomatosis (Blau syndrome) have been shown to have multifocal choroiditis lesions 45 (Fig 294) MEWDS patients will more often have unlateral disease, with yellow lesions at the level. Keywords Multifocal choroiditis, Chorioretinal lesions, Secondary CNV, Bevacizumab, Systemic immunosuppression, Case report Background Multifocal choroiditis (MFC) with panuveitis is a rare, recurrent white dot syndrome affecting myopic women in their third to fourth decades Symptoms include blurred vision, photopsia, or scotoma 1 Clinical find. The main finding is a peripapillary choroiditis that has a characteristic serpentine appearance In some cases, it involves the macula while sparing the peripapillary region The lesions are typically not multifocal as opposed to ampiginous or tuberculous serpiginouslike choroiditis The areas of active choroiditis appear gray or whiteyellow.
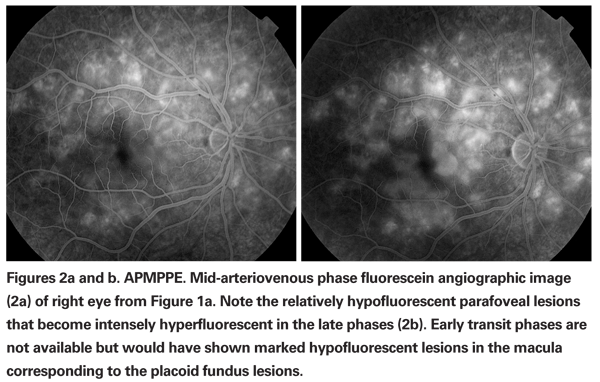
Acute posterior multifocal placoid pigment epitheliopathy (APMPEE) is differentiated by the level of the lesions, which is slightly more superficial than those in PIC On FA, APMPPE shows characteristic early hypofluorescence of the lesions in contrast to the hyperfluorescent lesions in PIC Furthermore, SRNV is a rare complication of APMPPE. Serpiginous choroiditis (SC) is a rare, bilateral, idiopathic inflammatory disorder that results in geographic destruction of the retinal pigment epithelium (RPE), retina, and choriocapillaris It is a chronic, recurrent, and progressive disease that typically affects patients 30 to 60 years of age. Multifocal Choroiditis Multifocal choroiditis (MFC) is a presumed autoimmune inflammatory disease primarily affecting myopic young women in their third to fifth decades Fundus examination shows small, round chorioretinal yellowish lesions (50–350μm in size) (see Figure 4a) that become atrophic in later stages The distribution of the scars is variable scattered or in aggregates widespread in the posterior pole and/or the periphery.
Multifocal choroiditis is a rare idiopathic inflammatory disease that affects the choroid Click on sample images to enlarge or download Multifocal Choroiditis, California, ICG OS, Courtesy Paulo Stanga, MD Multifocal Choroiditis, California, ICG OD, Courtesy Paulo Stanga, MD Multifocal Choroiditis, California, FA OS, Courtesy Paulo Stanga, MD. Placoid lesions of the retina may be secondary to a wide spectrum of acquired inflammatory conditions that have been reported as single entities with different presentation and clinical course These conditions include acute posterior multifocal placoid pigment epitheliopathy, persistent placoid maculopathy, serpiginous choroiditis, serpiginouslike choroiditis, relentless placoid. Multifocal choroiditis (MFC) occurs in the same age group as the other PICCPs, namely young to middle aged adults with women being predominantly affected 23 Lesions tend to leave scars and most of them are not spontaneously reversible, but active lesions seem to respond to inflammation suppressive therapy Photopsia is more frequent than in MEWDS and it may be present even when there is no clinical evidence of reactivation.
(FA) revealed bilateral perifoveal multifocal pinpoint hyperfluorescent leakage areas with a classical “gravitational tract” (Figure 5) Indocyanine green angiography was not included, because the dye not registered in Jordan Based on FAF and FA findings, the case was diagnosed as a case of chronic CSR, the corticosteroids were stopped. Multiple Evanescent White Dot Syndrome (MEWDS) is one of the diagnoses within the family of White Dot/ White Spot Syndromes, first described by Jampol L M and colleagues1 Within this diagnostic group are MEWDS, Acute Posterior Multifocal Placoid Pigment Epitheliopathy (APMPEE), Mulifocal Choroiditis and Panuveitis (MCP), Punctate Inner Choroiditis (PIC), and Birdshot Choriorretinopathy. PURPOSE To compare the utility of fluorescein angiography (FA) and optical coherence tomography (OCT) as diagnostic adjuncts in evaluating symptomatic patients with choroidal neovascularisation (CNV) due to multifocal choroiditis (MFC) METHODS Patients with CNV due to MFC were retrospectively evaluated in a consecutive fashion.
Purpose To compare the utility of fluorescein angiography (FA) and optical coherence tomography (OCT) as diagnostic adjuncts in evaluating symptomatic patients with choroidal neovascularisation (CNV) due to multifocal choroiditis (MFC) Methods Patients with CNV due to MFC were retrospectively evaluated in a consecutive fashion Fundus photography, FA, OCT and biomicroscopy were used to. Multifocal choroidopathy syndromes are rare disorders involving a primary pathologic process occurring at or near the level of the retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) with or without photoreceptor. Serpiginous choroiditis and infectious multifocal serpiginoid choroiditis Surv Ophthalmol 13 MayJun;58(3)332 ↑ Gupta V, Gupta A, Arora S, Bambery P, Dogra MR, Agarwal A Presumed tubercular serpiginouslike choroiditis clinical presentations and management Ophthalmology 03 Sep;110(9).
Keywords/Main Subjects Tuberculous Choroiditis Diagnosis Tuberculous Choroiditis Description of Image Here we are showing the fundus photo, FA, and ICG from a 51 year old female She was referred to uveitis clinic because her BCVA was /60 OS and she had a history of recurrent vitreous cell, floaters, and photophobia. Multifocal choroiditis and panuveitis syndrome Although HL may be negative in 4 to 10% of cases with birdshot chorioretinopathy, certain findings are in favor of multifocal choroiditis and panuveitis syndrome The hypofluorescent spots on ICG angiography in this case are smaller, of unequal sizes and more randomly distributed than what is. PURPOSE To compare the utility of fluorescein angiography (FA) and optical coherence tomography (OCT) as diagnostic adjuncts in evaluating symptomatic patients with choroidal neovascularisation (CNV) due to multifocal choroiditis (MFC) METHODS Patients with CNV due to MFC were retrospectively evaluated in a consecutive fashion.
FA/ ICG are also helpful in monitoring disease activity References Bock C, Jampol LM Serpiginous Choroiditis In Albert DM, and Jakobiec FA, (ed) Principles and Practice of Ophthalmology, WB Saunders Philadelphia 1994, pp Broekhuyse RM, Van Herck M, Pinckers AJLG, et al Immune Responsiveness to Retinal S. The choroiditis is characterized by multifocal white plaques in the choroid with little evidence of intraocular inflammation (Fig 118) It is an extrapulmonary form of pneumocystic disease usually seen in patients using a prophylactic inhalant for this condition, which prevents pulmonary involvement but does not provide systemic prophylaxis This has become a less common problem as the use of aerosolized pentamidine has decreased. To describe changes in the retina/choroid in patients with Serpiginous Choroiditis (SC) by Optical Coherence Tomography Angiography (OCTA) in a multimodal imaging approach Prospective, monocentric study of 24 eyes of 12 consenting patients diagnosed with SC, who underwent OCTA, which was analyzed and compared to other methods such as enhanced depth imagingOCT, fluorescein angiography.
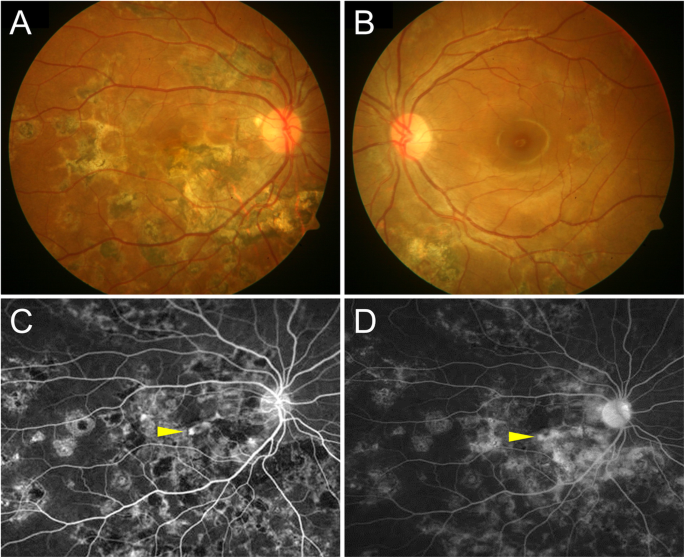
Choroidopathy (PIC) and multifocal choroiditis (MFC), are rare disorders which are included in the white dot syndrome spectrum, and they mostly occur in myopic patients 7, 8 Most researchers believe that PIC and MFC are the same underlying disease entity based on the ocular findings detected by recent multimodal imaging 7, 8 Inflammatory. PDF Purpose To report multimodal imaging findings in two cases of AIDSrelated cryptococcal chorioretinitis associated with uveitis and vasculitis Find, read and cite all the research you. The left eye (B) shows active serpiginous choroiditis On FA, active lesions (left eye) demonstrate early hypofluorescence (C) and late staining (d) Figure 3 Tubercular serpiginoid choroiditis A) Yellowish choroidal lesion in the inferior macula on initial presentation of tubercular serpiginoid choroiditis in a 42yearold Indian male.
Abstract A review of 28 cases of multifocal choroiditis with vitreous inflammatory cells demonstrates that these patients have chorioretinal scars similar to those in the presumed ocular histoplasmosis syndrome (POHS), but they have a low incidence of positive histoplasmin skin test reactions and calcified granulomata on chest xray films. Multifocal choroiditis (MFC) is a relatively uncommon bilateral inflammatory chorioretinopathy affecting Caucasian young women with myopia We present images from a case of completely unilateral multifocal choroiditis following EBVpositive mononucleosis that demonstrated a dramatic clinical response to immunosuppression A yearold woman with bilateral high myopia (−6D) and a documented.
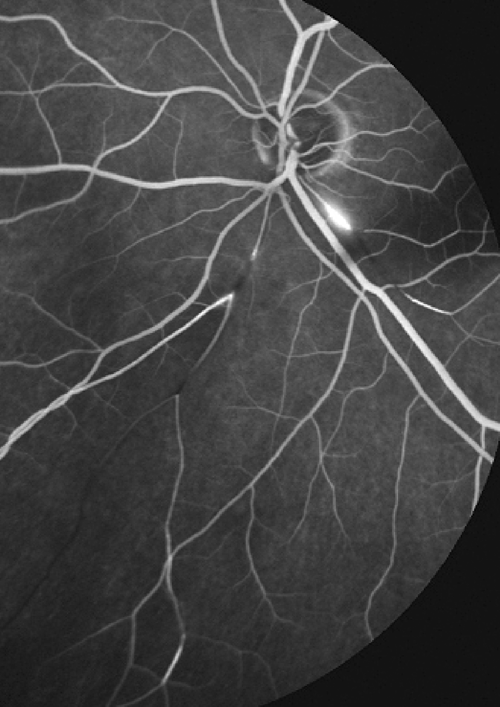
Advances And Potential New Developments In Imaging Techniques For Posterior Uveitis Part 2 Invasive Imaging Methods Eye

Multifocal Choroiditis And Panuveitis Ophthalmology
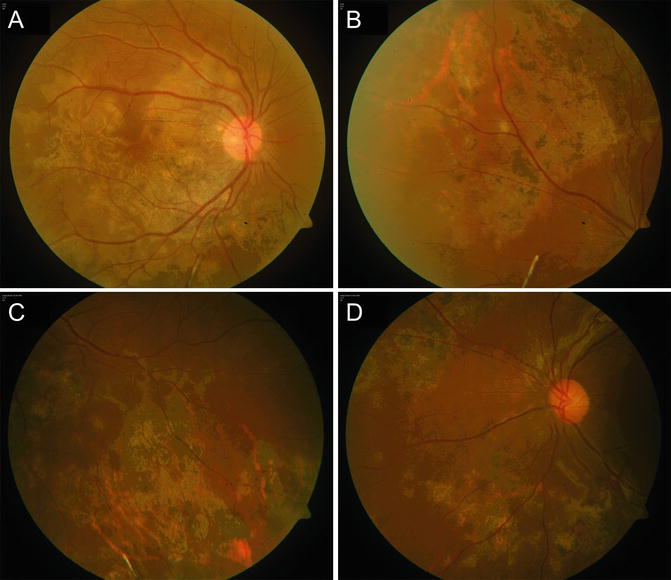
Tubercular Multifocal Serpiginoid Choroiditis Springerlink
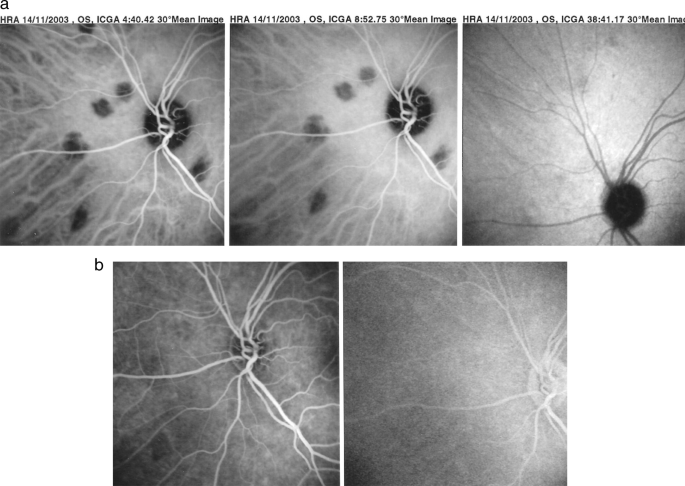
Advances And Potential New Developments In Imaging Techniques For Posterior Uveitis Part 2 Invasive Imaging Methods Eye

Multifocal Choroiditis Recognizing Pathology Optos

Role Of Autofluorescence In Inflammatory Infective Diseases Of The Retina And Choroid

Unilateral Multifocal Choroiditis Following Ebv Positive Mononucleosis Responsive To Immunosuppression A Case Report Bmc Ophthalmology Full Text

Retinal Physician Uveitis Diagnosis Management And Treatment
Diagnosis And Management Of Serpiginous Choroiditis American Academy Of Ophthalmology

Moran Core Fundus Photography Fluorescein Angiography And Indocyanine Green Angiography Of Tuberculous Choroiditis

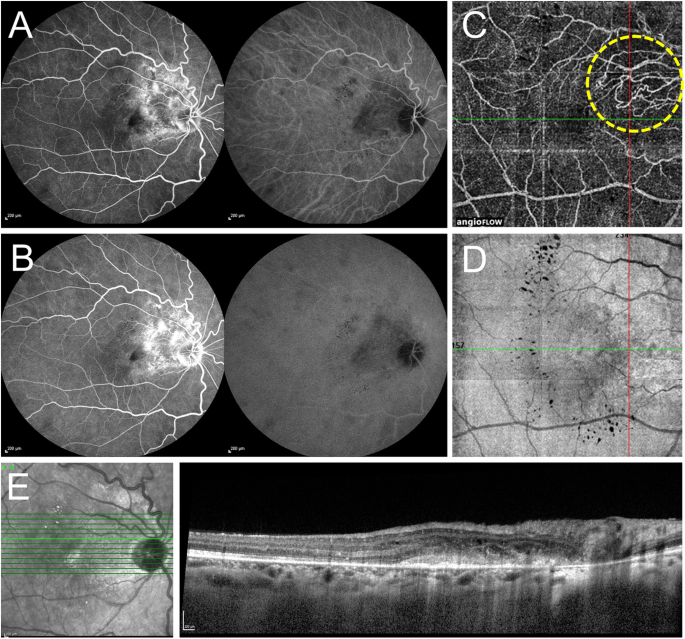
Choroidal Neovascularisation On Optical Coherence Tomography Angiography In Punctate Inner Choroidopathy And Multifocal Choroiditis British Journal Of Ophthalmology

How To Differentiate Myopic Choroidal Neovascularization Idiopathic Multifocal Choroiditis And Punctate Inner Choroidopathy Using Clinical And Multimodal Imaging Findings

Multifocal Choroiditis Recognizing Pathology Optos
Multifocal Choroiditis And Panuveitis Springerlink

Multifocal Choroiditis And Subretinal Fibrosis Syndrome Multifocal Choroiditis And Subretinal Fibrosis With New Subretinal Neovascular Membrane Retina Gallery Full Sized Retina Images
Choroiditis

Multifocal Choroiditis Subretinal Fibrosis Syndrome Multifocal Choroiditis Panuveitis With Subretinal Fibrosis Acute Phase Retina Gallery Full Sized Retina Images

Inflammatory Chorioretinopathies White Dot Syndromes Diagnosis And Management A Review Of The Literature Fiebai B Mohammed Sw Port Harcourt Med J

Moran Core Fundus Photography Fluorescein Angiography And Indocyanine Green Angiography Of Tuberculous Choroiditis
An Update On Inflammatory Choroidal Neovascularization Epidemiology Multimodal Imaging And Management Journal Of Ophthalmic Inflammation And Infection Full Text
Stock Image By2609 01b457hd Science Source Search Medical Scientific Stock Photos At Medicalimages Com

Fa In Multifocal Choroiditis As Shown In Figure 2b Extensive Icga Download Scientific Diagram

Choroiditis

Focal Choroidal Excavation In Multifocal Choroiditis And Punctate Inner Choroidopathy Ophthalmology

Case 5 A Fundus Photograph Left Eye Of A year Old Man With Download Scientific Diagram

Choroiditis
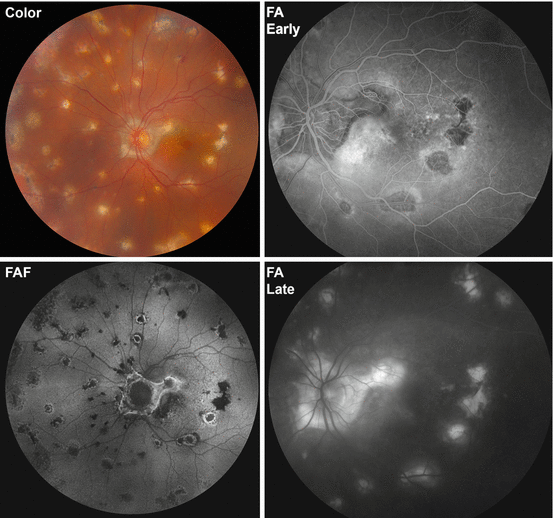
Multifocal Choroiditis And Panuveitis Springerlink

Chorioretinitis Article

Choroiditis

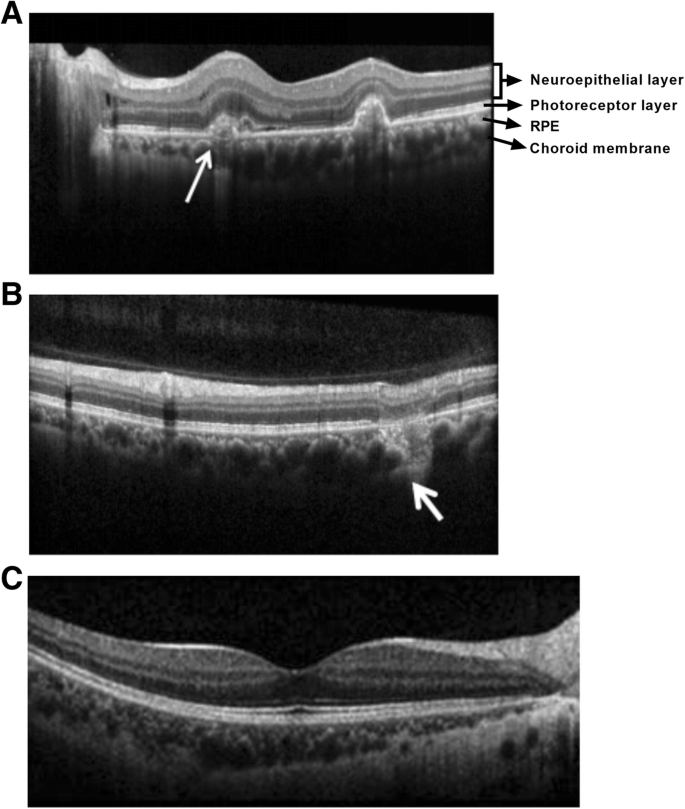
Spectral Domain Optical Coherence Tomography Angiography Findings In Multifocal Choroiditis With Active Lesions American Journal Of Ophthalmology

Multifocal Choroiditis Recognizing Pathology Optos

View Image

Indocyanine Green Angiography In Posterior Uveitis
.jpg/image-full;max$643,0.ImageHandler)
Multifocal Choroiditis And Panuveitis Syndrome Retina Image Bank

How To Differentiate Myopic Choroidal Neovascularization Idiopathic Multifocal Choroiditis And Punctate Inner Choroidopathy Using Clinical And Multimodal Imaging Findings

Sciencecentral
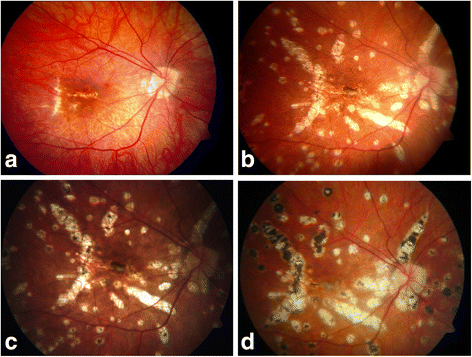
Course Of Disease In Multifocal Choroiditis Lacking Sufficient Immunosuppression A Case Report Journal Of Medical Case Reports Full Text

Multifocal Choroiditis Recognizing Pathology Optos

Jaypeedigital Ebook Reader
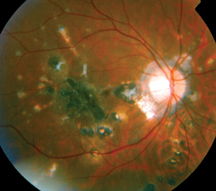
Multifocal Choroiditis Vs Pic Variations On A Theme

White Dot Syndromes
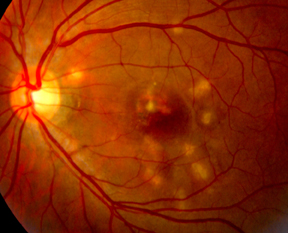
Multifocal Choroiditis Vs Pic Variations On A Theme
Early A And Late B Phase Of Fluorescein Angiography Fa Of A Download Scientific Diagram

More Than Uveitis Retina Today

Figure 2 From Multi Modal Imaging And Anatomic Classification Of The White Dot Syndromes Semantic Scholar

White Dot Syndromes Ento Key
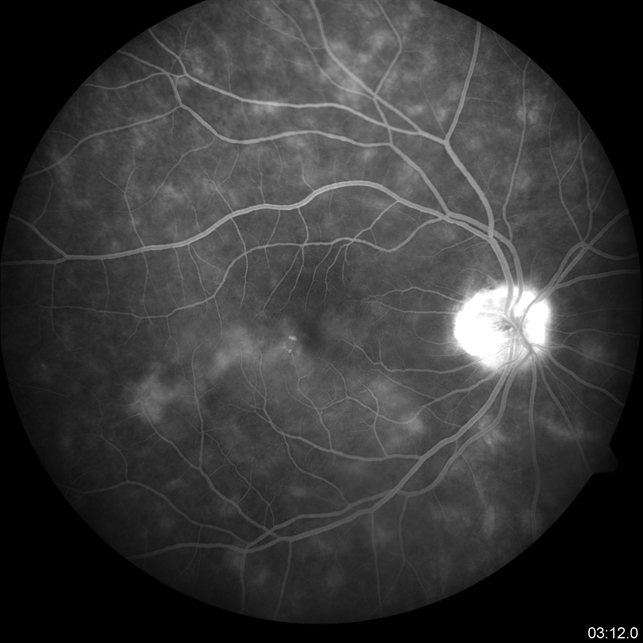
Multifocal Choroiditis Retina Image Bank

Multifocal Choroiditis Subretinal Fibrosis Syndrome Multifocal Choroiditis Panuveitis With Subretinal Fibrosis Acute Phase Retina Gallery Full Sized Retina Images

Serpiginous Choroiditis And Infectious Multifocal Serpiginoid Choroiditis Abstract Europe Pmc

Moran Core Fundus Photography Fluorescein Angiography And Indocyanine Green Angiography Of Tuberculous Choroiditis

How To Differentiate Myopic Choroidal Neovascularization Idiopathic Multifocal Choroiditis And Punctate Inner Choroidopathy Using Clinical And Multimodal Imaging Findings
Recognizing The White Dot Syndromes

White Dot Syndromes Ento Key

Multifocal Choroiditis Panuveitis 32 Year Old Woman Cnvm Os Recurrs 4 Years After Initial Therapy Avastin Punctate Inner Choroidopathy Recurrent Cnvm 4 Years After Initial Treatment Left Eye Fluorescein Angiogram

Retinal Imaging In Uveitis Sciencedirect

Choroidal Neovascularisation On Optical Coherence Tomography Angiography In Punctate Inner Choroidopathy And Multifocal Choroiditis British Journal Of Ophthalmology
An Update On Inflammatory Choroidal Neovascularization Epidemiology Multimodal Imaging And Management Journal Of Ophthalmic Inflammation And Infection Full Text

Icga In Multifocal Choroiditis Icga Shows Widespread Non Perfusion In Download Scientific Diagram

Retina Image Set 2 Flashcards Quizlet

Multifocal Choroiditis Recognizing Pathology Optos

Idiopathic Multifocal Choroiditis Eyewiki
Multimodal Imaging Of Apmppe Related Disorders

View Image
Imageology Features Of Different Types Of Multifocal Choroiditis Bmc Ophthalmology Full Text

Sequential Octa Of A Multifocal Choroiditis Patient After Steroid Download Scientific Diagram

Retinal Imaging In Uveitis Sciencedirect

White Dot Syndromes

Feb 17
Intravitreal Methotrexate For The Treatment Of Choroidal Neovascularization In Multifocal Choroiditis Eye

Successful Treatment Of Tubercular Multifocal Serpiginous Like Choroiditis Without Use Of Anti Inflammatory Drugs A Case Report With Multimodal Imaging Sciencedirect

Multifocal Choroiditis In A Diabetic Patient Scienceopen

Multimodal Imaging Of A 44 Year Old Man With Serpiginous Choroiditis Download Scientific Diagram
Choroiditis

Multimodal Imaging Of The White Dot Syndromes And Related Diseases Abstract Europe Pmc
Multifocal Choroidopathy Syndromes Overview Multifocal Choroiditis Acute Posterior Multifocal Placoid Pigment Epitheliopathy

Punctate Inner Choroidopathy

Successful Treatment Of Tubercular Multifocal Serpiginous Like Choroiditis Without Use Of Anti Inflammatory Drugs A Case Report With Multimodal Imaging Sciencedirect

Indocyanine Green Angiography In Posterior Uveitis Abstract Europe Pmc

Choriocapillaris Involvement In Acute Syphilis Posterior Placoid Chorioretinitis Is Responsible For Functional Impairment And Points Towards An Immunologic Mechanism A Comprehensive Clinicopathological Approach Herbort Cp Papasavvas I Mantovani A
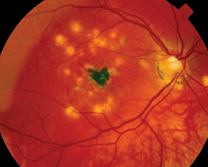
Multifocal Choroiditis Vs Pic Variations On A Theme

Multifocal Choroiditis Unknown Etiology The Retina Reference

Multifocal Choroiditis Recognizing Pathology Optos

Feb 17

White Dot Syndromes



